


The Tesla Coil is one of Nikola Tesla's most famous inventions originally developed to explore wireless transmission of electrical energy. It’s a type of resonant transformer circuit that produces high-voltage, low-current, high-frequency alternating current (AC) electricity.
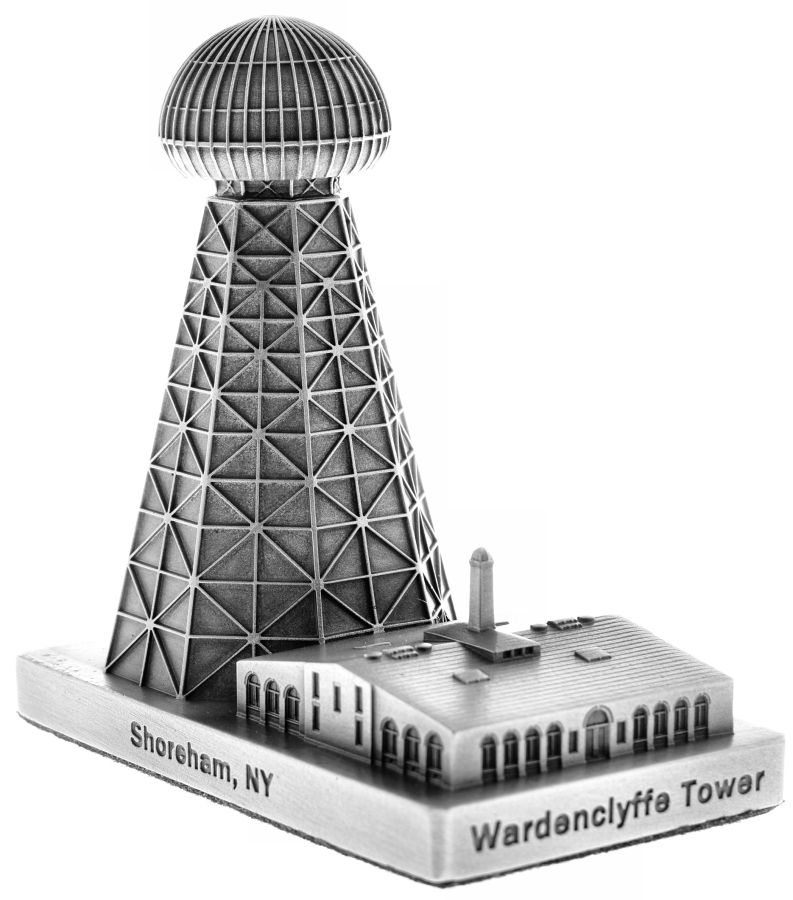

The Wardenclyffe Tower, also known as Tesla Tower, was an early wireless transmission station designed, intended the tower to be the first broadcast station and a transatlantic wireless communication station. He envisioned it transmitting messages, telephony, and even power wirelessly across the globe. and built by Tesla in Shoreham, New York.
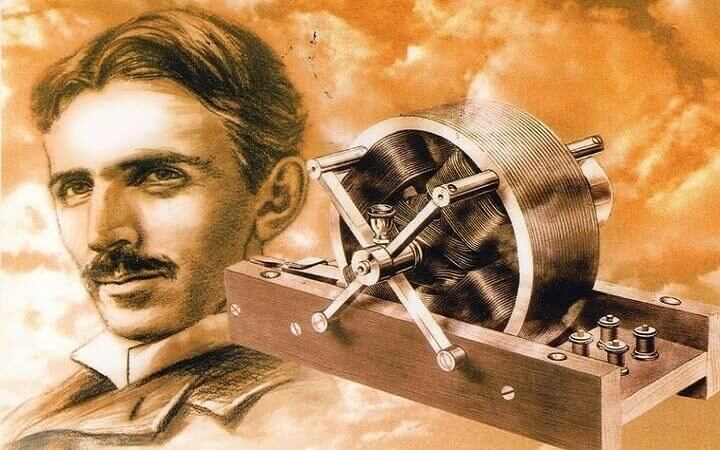
Tesla's AC (alternating current) system is a method of electrical power transmission that rapidly reverses direction and is the standard for electricity distribution today. The AC system was designed to replace direct current (DC) systems for long-distance electrical power distribution. AC could be easily transformed to different voltages, allowing for efficient transmission over long distances. It became the foundation of the modern electrical grid, allowing electricity to be delivered efficiently to homes and industries around the world.